Blog
Where Will InsurTech Have the Most Impact on Brokerages and Insurance Products?
The intersection of technology and insurance—referred to as InsurTech—comes in many forms, from startups that aim to disrupt the healthcare industry to simple robotic process automation for things like claims handling.
And it's growing at a rapid pace; in Q2 2019 there were 69 InsurTech investment deals with a total value of $1.4 billion announced, according to CB Insights Quarterly InsurTech Briefing.
And yet, we're still just scratching the surface of how technology can transform and disrupt a more traditional industry like insurance.

As technologists who have an insider's perspective on the insurance sector, there are two distinct areas where we see technology potentially impacting the market most: brokerages and insurance products.
We also see five emerging technologies that will enable the growth and adoption of InsurTech:
- Artificial intelligence
- Internet of Things
- Predictive analytics
- Blockchain
- Quantum computing
With that, let's take a closer look at how technology is coming together to transform a more than 300-year-old industry.
InsurTech and Market Transformation
The Brokerage Transformation
How will InsurTech impact brokerages?
We're already seeing digital brokerages pop up—take Insureon, for example. These types of companies may cause traditional brokerages to become disintermediated or obsolete for small business insurance, and personal lines of insurance especially.
More and more, an insurance cycle without a human touch will come into play, connecting the company or person seeking the insurance directly to the insurance company. Unless brokers act swiftly in the face of new technology, their value will be decimated.
Small commercial accounts represent about $100 billion in direct written premiums. Yet incumbent insurers have largely failed to provide digital solutions that satisfy this type of consumer.
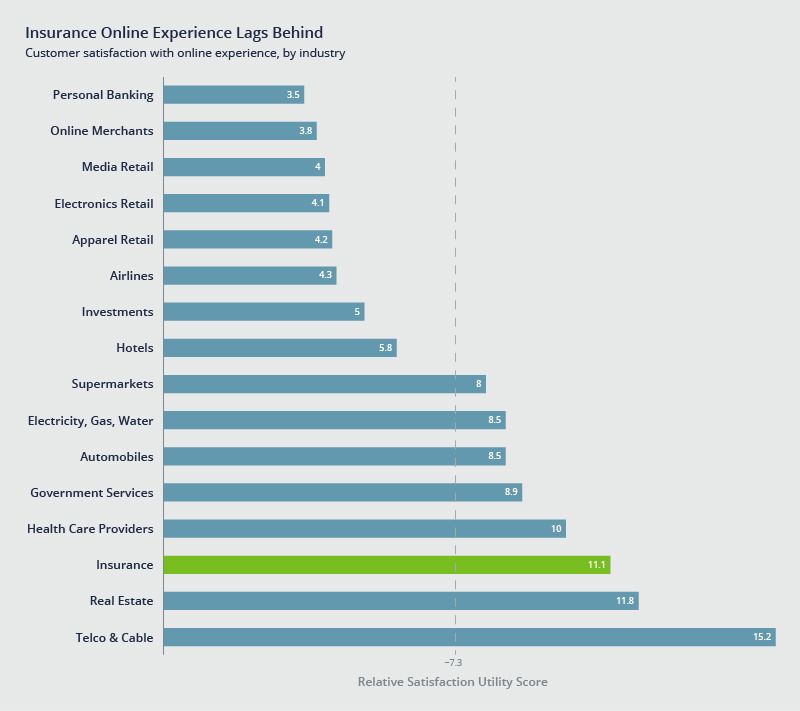
And large brokers are also ignoring a potentially profitable percentage of business by not successfully deploying digital solutions to better serve those small commercial accounts.
Because small business insurance is a much simpler transaction than the more strategic insurance programs that require professional expertise, there's an opportunity to serve these emerging businesses and consumers by digitizing our brokerages.
The digital broker is one trend we do not see going away. So as a traditional broker, why not play a part in creating your own digital broker platform, so we as an industry can be creators, owners, and managers of the technology? This would allow us to funnel at least a portion of our small business insurance through a platform and avoid investing the same amount of human resources that we do on some of our largest and most strategic lines.
The Product Transformation
Insurance as a product is also transforming through InsurTech in many ways. One dramatic shift in how insurance products are sold is the on-demand insurance market.
When we think about conventional insurance, it is at minimum an annual commitment (or a lifelong affair when it comes to life insurance). In essence, this model looks at insurance as a time-bound commitment.
On-demand insurance allows consumers to purchase insurance via apps, for example, whenever they need it and with no long-term contracts. In comparison to traditional insurance, this model is event-based, i.e., it can be activated in anticipation of specific events and/or activities.
One such example is Trōv. Consumers can purchase single item insurance protection to use while they are on a trip or as an extended warranty. Buyers can swipe their insurance on or off through an app in what Trōv calls “micro-duration” policies, and are only charged for the time it is on.
On-demand insurance is another InsurTech venture that caters to a new generation of consumers that want the benefit of the product without the long-term commitment.
InsurTech and the Use of Emerging Technologies
What will be the most important technologies in InsurTech to support the market transformations discussed here and beyond?
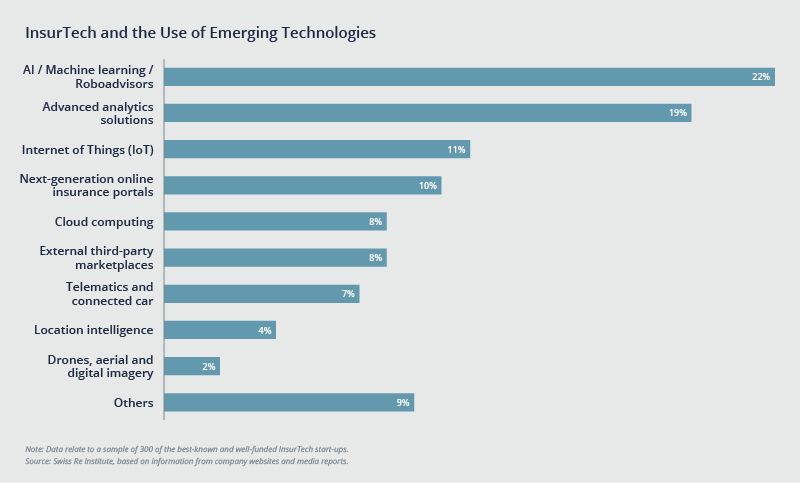
According to Swiss Re Institute research, technology areas that InsurTech startups are focusing on the most include artificial intelligence (AI), followed by analytics then Internet of Things (IoT).
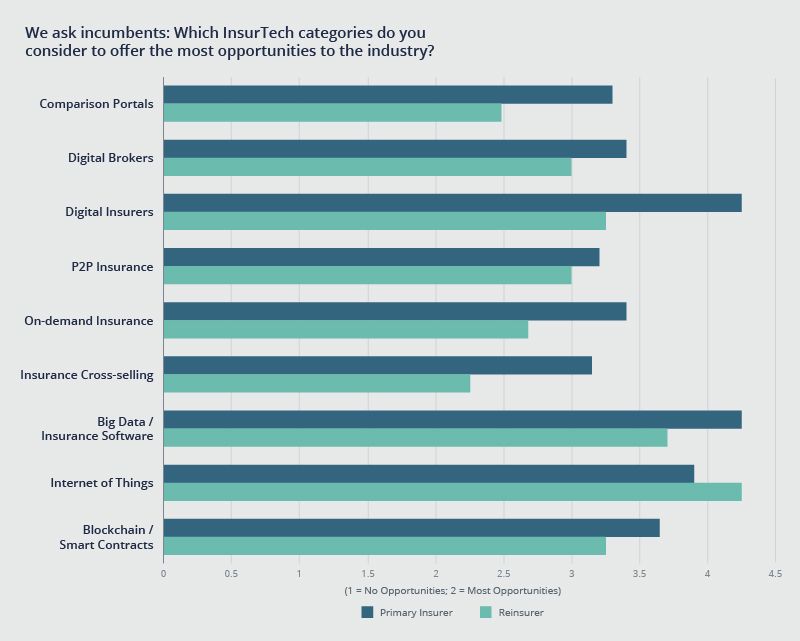
Insurance incumbents believe that things like big data and IoT offer the most opportunities to the industry, based on research conducted by the Institute of Insurance Economics.
From our perspective, we see five types of technology that will enable innovation in every corner of the insurance market, which we'll discuss briefly next.
1. Artificial Intelligence
AI in insurance has been able to enhance things like customer experience and process optimization. It is even being used to help detect insurance fraud.
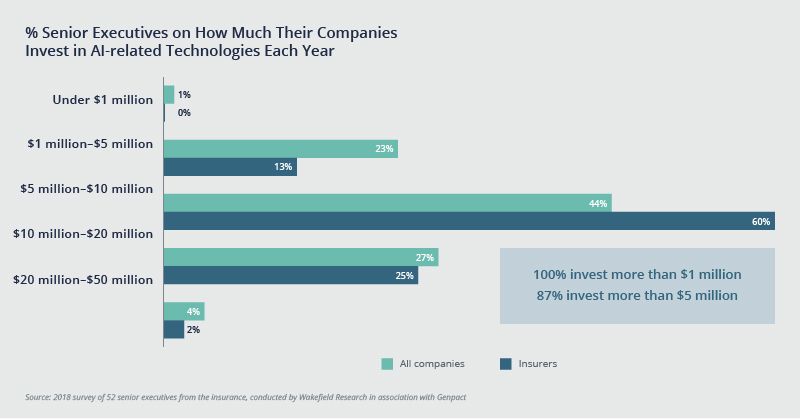
Research conducted by Genpact in 2018 found that 87% of insurers are investing more than $5 million in AI each year.
Coming from a broker's perspective, investing in AI for the claims handling process could pay dividends.
Let's say you have a claims submission platform enabled for clients. Typically, there is still some level of human intervention. An AI solution could take that to the next level by eliminating the manual step of attaching the right documents to the claim submission and routing to the insurer.
According to our analysis here at Woodruff Sawyer, 35% of claims activities can be automated using this AI-driven approach; correspondingly, cycle times could reduce by as much as 40% by automating these predominantly human-intensive process steps.
2. Internet of Things
By 2020, the IoT will comprise about 30 billion connected devices. And the insurance industry along with its consumers is benefiting from this connectedness.
So far, the insurance industry has mostly made use of IoT through things like telematics for car insurance, whereby drivers can install a device in their car that monitors driving behaviors with the promise of reduced rates.
But there is certainly more innovation on the horizon. For example, Google is looking to pair its smart home brand, Google Nest, with insurers to “blend technology and hardware with insurance.”
And there are plenty of other IoT insurance partnerships that are helping consumers save money on insurance.
With the sheer amount of data coming from IoT, the insurance sector has a huge opportunity to better serve consumers. Say, for example, a consumer purchases home insurance for a specific rate premium. A month after activating the insurance contract, the consumer installs two carbon monoxide detectors in the house.
In an IoT-enabled world, the carbon monoxide detector devices could be wi-fi enabled to send their data to the insurer informing them that the consumer's home is more secure than before.
This could then trigger an automated rate adjustment at the insurer, and the premium to be paid by the consumer could get reduced automatically the following month.
3. Predictive Analytics
Insurers have been using predictive analytics for some time for things like modelling risks. Though its adoption today can enable a great many more things, as this article points out.
We're already seeing companies like EigenRisk pop up that offer analytics which enables brokers and their clients to better model their own natural catastrophe risks. This, in turn, can help brokers essentially pre-underwrite the risk and in some cases, negotiate better rates.
The possibilities are seemingly endless with how predictive analytics can enhance the insurance industry. One area where we see a great need for analytics is brokerages being able to help insurers quote better.
We see thousands of insurance quotes per day come in. And from those quotes, only a small percentage are recommended and then chosen by our clients.
Using all that data, predictive analytics could show, for example, which quotes were actually selected within a specific subset of companies for a particular region.
The analysis of this data could enable the insurers to learn how to alter their product offerings in order to be more attractive to those seeking insurance.
4. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is essentially a digital ledger of record keeping that cannot be corrupted, and it has many applicable scenarios.
Startups are emerging that use blockchain technology in insurance for multiple use cases, like fraud detection, automated quoting of homogeneous Business Owner Policy (BOP) coverage, and internal processes such as policy checks, First Notice of Loss (FNOL), and financial reconciliation.
5. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a totally new way of computing with advanced processing powers. (If this is a newer concept to you, IBM offers a simplified explanation of it here.)
Quantum computing has the ability to take massive, complex datasets and make fast calculations—more efficiently than traditional computing.
It is already being used in some industries, and has the potential to make a massive impact on many others—insurance being one of them.
None of the other four emerging technologies we mentioned in this article are able to truly disrupt the industry until we are able to process the massive amounts of data that insurers and brokers generate every day. That is one of the promises of quantum computing.
What may take two hours of traditional computing, for example, can be accomplished in just one second with quantum computing. Imagine the possibilities.
In essence, the insurance sector is at an inflection point from a technology standpoint—the question is no longer whether or not to digitize; rather, it is about how much to invest mindshare into digital transformation.
Woodruff Sawyer endeavors to be on the cutting edge of the intersection of insurance and technology. For more information, reach out to your Account Team.
Table of Contents












