Blog
Property and Casualty Risks Faced by Data and Analytics Service Providers
Company leadership must develop a deep understanding of data and analytics risks and implement both proactive prevention measures and reactive response plans.
With the explosive growth of data over the last decade, a new industry has emerged: data and analytics services. In an article published in December 2022, Acumen Research and Consulting estimated the global size of the industry at $31.8 billion and expects it to grow to $329.8 billion by 2030 at a 29.9% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). The companies in this industry are engaged in analyzing large volumes of data and delivering insights based on time series trends, hidden patterns, correlations, variability, and other properties.
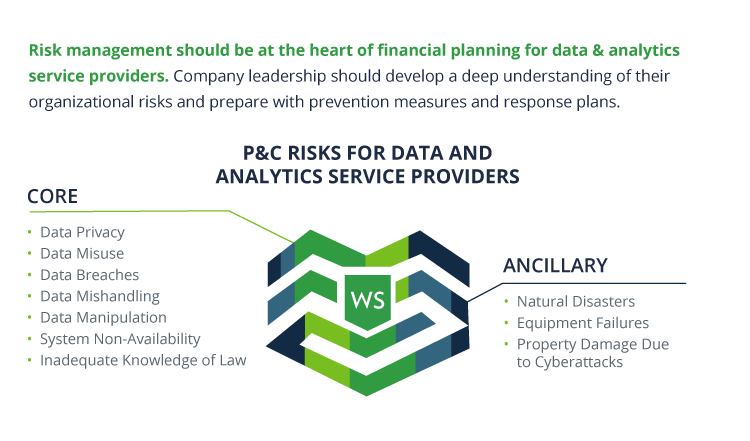
This rise of data and analytics service providers has transformed the business landscape in multiple industries. Be it financial analytics for investor insights, healthcare analytics involving patient information, or social media data for customer targeting, the power of analytics in optimizing business strategy decisions and guiding investments is recognized today in all sectors. With the growing reliance on data-driven insights and decision-making, data and analytics service providers have become vital partners for businesses across industries. However, the industry itself also faces unique property and casualty risks that must be addressed and managed to ensure its continued success. This article will explore these types of risks through a lens of core versus ancillary risks and potential mitigation methods.
Core Risks for Data and Analytics Service Providers
Data and analytics service providers face unique and complex casualty risks different from other types of businesses. Due to the nature of their business, a data and analytics service provider’s employees access or receive sensitive personal, financial, or health information from clients to provide valuable insights. Hence, data security, service, privacy, and operational risks are the most significant risks to consider. Note that such risks are subject to intrusion and malicious activity impacting data security and privacy that can lead to substantial financial and reputation loss.
Here are five essential factors to consider:
- Data breaches
- Data mishandling
- Data manipulation
- System non-availability
- Inadequate knowledge of applicable laws
Data Breaches
When sensitive personal, financial, or health information is compromised, it can lead to loss of trust from customers and clients, legal and regulatory penalties, and even business shutdowns.
For example, let's assume a data service provider (company A) works as a consultant for a healthcare organization (company B). Company A experiences a data breach that exposes sensitive patient information, including medical records, Social Security numbers, and financial information. This data breach puts the affected patients at risk of identity theft and financial fraud, exposing company B to significant liability and reputational damage.
As a result of the breach, company B sues company A. Additionally, affected patients file a lawsuit against companies A and B, where such loss liability may translate into contractual liability for company A. In addition to direct financial losses from lawsuits and settlements, both companies can suffer irreparable brand image and reputational harm. Therefore, it's important for data and analytics service providers to have a robust financial risk management framework in place.
Data Privacy, Data Mishandling, and Data Misuse
Data service providers must be aware of the different types of data mishandling. It can take many forms, including:
- Unauthorized access: This problem includes scenarios when an employee or outside party gains access to sensitive data without proper authorization or when sensitive data is shared with parties who do not have appropriate authorization to access it, such as competitors or unauthorized third parties.
- Inaccurate data entry: Entering incorrect data into a system, resulting in inaccurate or unreliable results, would fit this type of mishandling.
- Data theft: When data theft occurs, it indicates a lack of adequate security and data handling. For example, in 2017, Equifax’s alleged failure to patch the vulnerability of web software allowed hackers to exploit and gain access to sensitive data.
- Data loss: This issue occurs when data is accidentally or intentionally deleted or destroyed, resulting in the loss of important information.
- Improper disposal: Examples include situations where data is not disposed of properly, such as when hard drives or other storage devices are not wiped clean before disposal.
An example of data misuse and resulting loss occurred in 2018 when a political consulting firm, Cambridge Analytica (and its parent company SCL group), closed operations due to its involvement in a data privacy scandal. The firm used data collected through its app using a popular social media platform to create political ads and messages targeted at specific groups of voters during the 2016 US presidential election. As a result, the firm gained unauthorized access to the personal data of nearly 270 million users without their consent. The data was allegedly used to influence voter opinion during the election.
As a result of the scandal, Cambridge Analytica and its parent company faced several lawsuits, including a class-action case in the US. The company was accused of violating users' privacy rights and misusing their data for political gain. Cambridge Analytica and SCL group ultimately filed for bankruptcy and closed their doors officially on May 1, 2018.
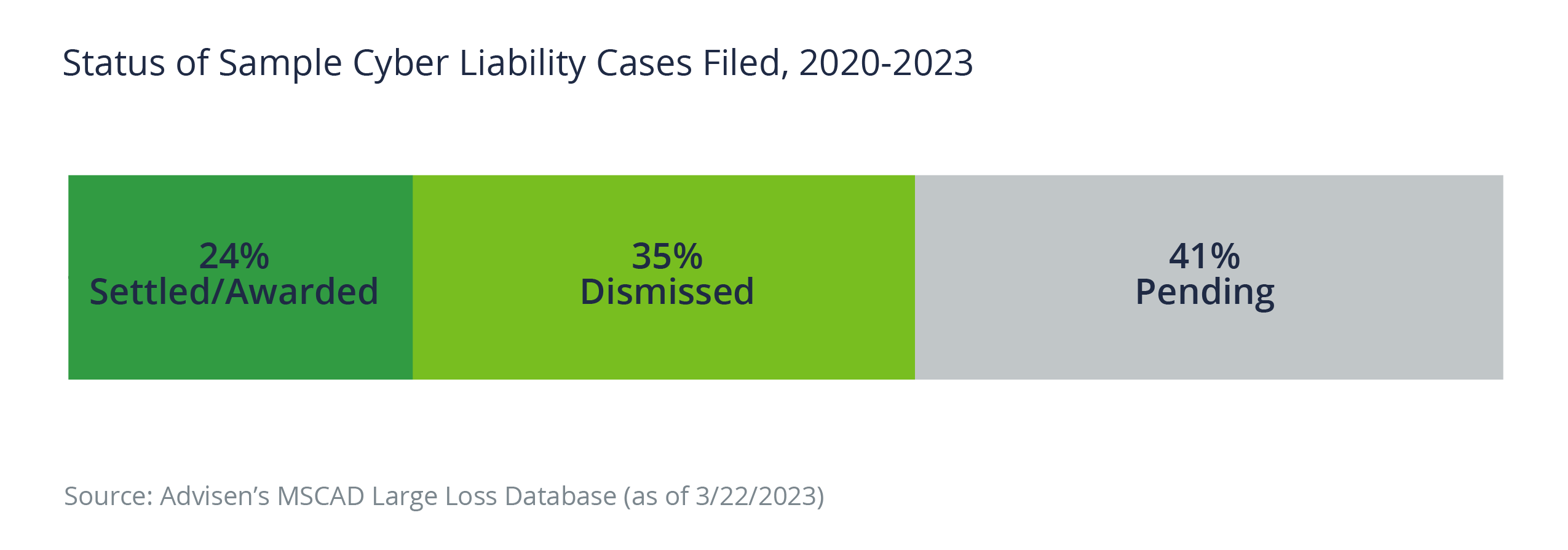
Annually, in the United States, more than 2,000 liability cases are filed that are publicly known and relate to data privacy and disclosure problems. This data includes all industries that are involved in handling third-party data. Data from Advisen shows that between 2020 and 2022, approximately 4,873 cases were filed relating to data privacy and mishandling across all industries in the US. While 41% of filings are pending, 24% of such filings resulted in some monetary settlement or award. Only 1.5% of the cases were resolved for more than $1 million, but these high-cost settlements amounted to 99% of the total loss amount.
As the data and analytics services industry grows and becomes an integrated part of other businesses, corporate leaders should care about the casualty risks related to data privacy, data mishandling, and data misuse. Such risks are a natural and critical threat to their company’s balance sheet and existence.
Data Manipulation and Accuracy
Another important consideration is the risk of data manipulation. This risk can include the potential for data to be altered, deleted, or corrupted, impacting the accuracy of the results generated by data and analytics service providers.
Data manipulation and the resulting casualty loss can occur in the financial sector. For example, imagine a data and analytics service provider is hired to analyze a company's financial data and provide insights to investors. If the provider manipulates the data to show better financial performance, it could result in investors making decisions based on false information.
If the manipulated data is discovered, it could lead to a significant decline in the company's stock price, causing a financial loss for investors. In this scenario, the data and analytics service provider could be held liable for the resulting casualty loss.
System Non-Availability Risks
Data and analytics service providers also face a financial risk when their services become unavailable for any underlying reasons. For example, let’s say you provide marketing analytics services and dashboards and experience a widespread outage that takes more than a week to fix.
In this scenario, your clients cannot access critical data and insights about their marketing, leading to a loss of productivity and potential revenue. Additionally, some businesses may have made decisions based on incomplete or outdated data, potentially leading to poor performance or financial losses. Therefore, ensuring reliable and redundant data analytics systems and mitigating the potential associated risks is essential.
Risks Due to the Lack of Awareness of Data Privacy and Intellectual Property Laws
Insufficient awareness of data privacy and intellectual property laws also can lead to casualty losses for data and analytics service providers. For example, in 2020 and 2021, a healthcare data and analytics company providing billing and accounting services for hospitals was sued in multiple states for allegedly posting the sensitive medical information of over 2,000 patients on a publicly accessible website without obtaining their consent or giving them the opportunity to opt out.
The lawsuits sought penalties of varying degrees for each violation of the state's data privacy laws and an injunction to prevent the company from engaging in similar practices in the future. The incident resulted in significant financial losses, damaged the company's reputation, and eroded trust among its clients and customers.
Data and analytics service providers often use open-source software. Also, they are adept at exploiting and using hidden portions of the applications' code to create tailored solutions for their clients. Intellectual property disputes and copyright infringements can occur in such cases, leading to significant financial risk.
In conclusion, the casualty risks associated with data and analytics service providers are numerous and can be severe. However, by minimizing these risks, such as investing in cybersecurity measures, implementing robust data protection protocols, and increasing awareness of the potential for legal and regulatory challenges, data and analytics service providers can protect their bottom line and ensure the success of their operations.
Ancillary Risks for Data and Analytics Service Providers
Property risk refers to the potential loss or damage of physical assets, such as equipment, buildings, and other tangible property. For data and analytics service providers, the property at risk goes beyond ordinary physical assets. Today, more and more companies prefer the hybrid data infrastructure, with an optimal balance of costs and speed between cloud and on-premises equipment. Hence, the property risk relates to the on-site hosted critical data infrastructure, such as data center servers, storage devices, employee desktops and laptops, and related equipment.
Here are three crucial perils that impact the property risk of data and analytics services providers:
- Natural disasters
- Equipment failure
- Cyberattacks
Natural Disasters
One property risk data and analytics service providers face is natural disasters. Disaster recovery is part of standard practices for large organizations. However, do all organizations engage in consistent practices?
New and emerging data and analytics service providers can be impacted severely by floods, earthquakes, and hurricanes. These events, which are occurring more frequently due to climate change, can result in significant damage to equipment and infrastructure. Some of the hardware issues that natural disasters can cause include:
- Facility damage: Natural disasters such as earthquakes or hurricanes can cause physical damage to buildings and facilities housing the data infrastructure.
- Water damage: Flooding from storm surges, rivers, dams, or water channels due to excessive rains can cause irreversible water damage to hardware, such as motherboards, hard drives, or other critical components.
- Heat damage: Wildfires or excessive heat waves can harm temperature-sensitive components such as central processors.
- Power surges and outages: Lightning strikes or other electrical surges caused by natural disasters can cause power fluctuations, burning hardware or making it unstable or unresponsive.
- Dust or debris damage: Tornadoes and high winds can cause dust or debris to enter a device, interfering with performance and causing slowdowns or complete failures.
Equipment Failure
Another property risk faced by data and analytics service providers is a variety of equipment failures. The high demand for data significantly strains the equipment and infrastructure, increasing the risk of equipment failure.
For example, solid-state drives promise speeds higher than traditional spinner hard drives. However, a high number of reads/writes to solid-state drives degrades the physical capacity of the drive and can cause spotty block failures. Such degradation can corrupt a portion of files and lead to lost data and downtime.
Here are other potential equipment failure problems:
- Faulty power distribution: Poor power distribution equipment can lead to power surges that can burn the server motherboards or tiny capacitors that run the computer central systems.
- Cooling system failures: Data centers generate a lot of heat, which must be managed using cooling systems. If the cooling systems fail, the temperature in the data center can rise quickly, leading to equipment failure and data loss.
- Hardware failures: Ordinary hardware failures can occur for a variety of reasons, including manufacturing defects, wear-and-tear, and overheating. Hardware failures can lead to downtime and the loss of critical data.
- Network failures: Data centers rely on network equipment to communicate with servers and storage devices. Network equipment failures can cause connectivity issues and data loss.
Cyberattacks
With the increasing volume of data, data and analytics companies are a prime target for cybercriminals looking to steal sensitive information or disrupt operations. In addition to software or network accessibility issues, cyberattacks can create various hardware issues that impact the performance, security, and availability of computing devices. Note that the damages to property due to cyberattacks are not insurable under a core property policy.
Some hardware issues that cyberattacks can cause include:
- Physical corruption: A cyberattack, such as a malware infection, can damage hardware components, potentially corrupting the sectors of a hard drive or blocks of a solid-state drive, motherboard, or other critical components sectors.
- Overheating: Cyberattacks can cause computing devices to work harder than usual, overheating and damaging the processor or other temperature-sensitive hardware components.
- Lockouts: A cyberattack could lock the physical storage permanently, rendering it useless.
Cyberattacks could also extend to individuals’ hardware, including desktops and laptops used by employees on a large scale with similar impact.
Overall, these property-related perils can significantly impact the availability and integrity of information stored in data centers. Not only would the company face property loss, but the downtime and time to restore can also lead to a significant business loss for their clients and potentially create service and operational risks.
How Data and Analytics Service Providers Can Lower Their Risk
Here is a brief overview of possible measures data and analytics service providers can take to lower their risk.
- Develop and implement robust data protection and privacy policies and procedures.
- Conduct site risk audits using loss control specialists from cyber, casualty, and property lines of business. Implement mitigation recommendations timely.
- Stay up to date with new security technology and robust cybersecurity measures like firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, and adopt the necessary measures to guard against emerging risks.
- Invest in thorough quality control processes and take steps to ensure that all products and services are delivered with the highest levels of accuracy and reliability.
- Use secure data storage solutions and backup and recovery systems to ensure that any lost or corrupted data can be quickly restored.
- Invest in strict data protection protocols like encryption and secure data storage solutions.
- Conduct regular data risk assessments and implement appropriate security measures.
- Train employees and contractors on data handling and privacy policies and procedures.
- Learn about legal and regulatory compliance measures and work with experienced counsel to navigate the complex legal and regulatory landscape.
- Implement up-to-date legal and regulatory requirements and comply with applicable laws and regulations.
- Monitor and audit data access and use and limit access to sensitive data to those who require it.
- Obtain appropriate insurance coverage for insurable risks. Note that effective insurance placements require brokers who are good at quantifying exposures, assessing risk tolerance, matching policy types to the coverage, and evaluating relevant risk financing strategies.
- Use encryption and other data protection technologies to secure data in transit and at rest.
- Conduct regular disaster recovery and business continuity planning to minimize data loss and downtime.
By taking these and other risk mitigation steps, data and analytics service providers can reduce their exposure to a range of data-related risks and minimize the potential for casualty losses.
If you want to quantify your property and casualty risks, understand if these risks are insurable, and discuss appropriate insurance program design, contact your Woodruff Sawyer account team.
Table of Contents












